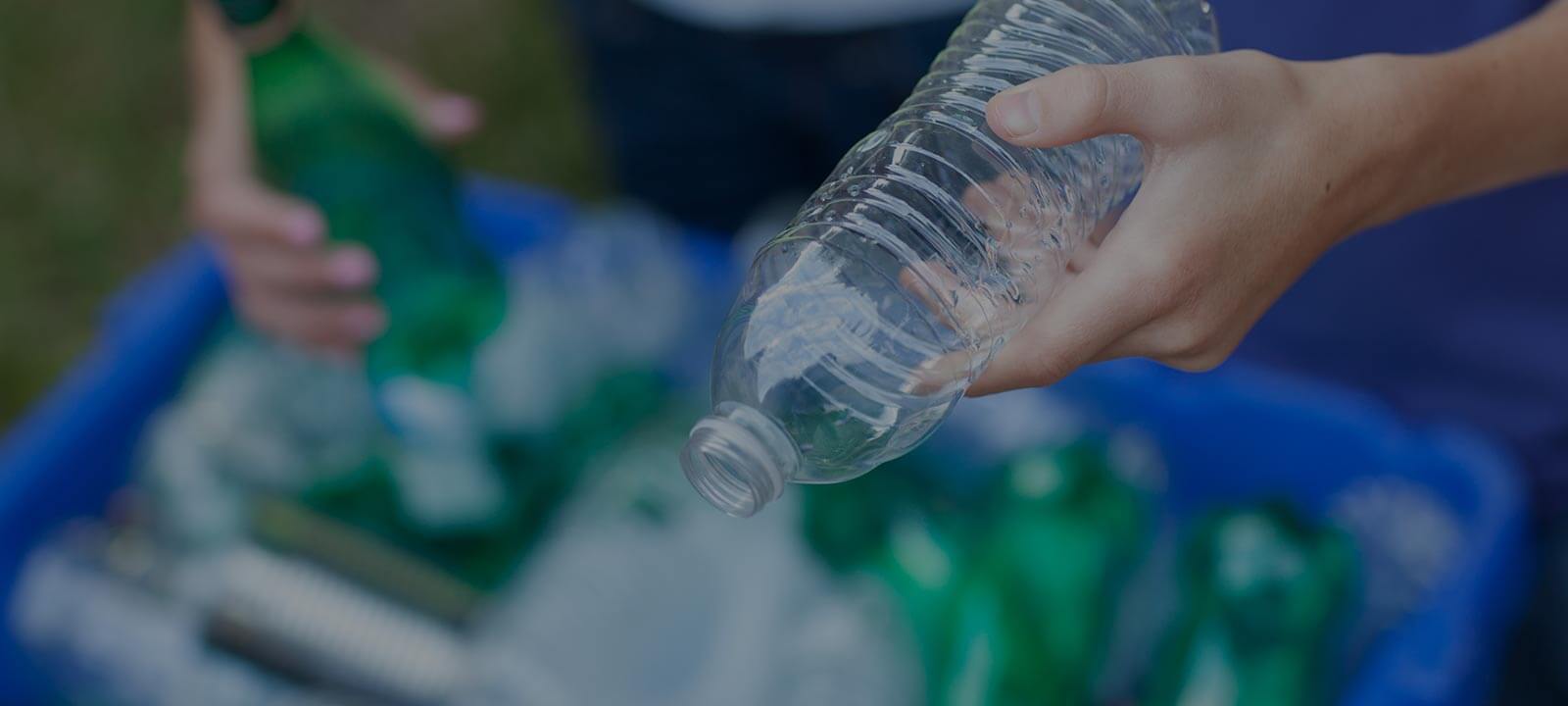
Green Options for Substituting Plastic
Posted on 30/08/2025
Plastic, once hailed as a revolutionary material, has become a major environmental challenge. Its ubiquitous nature and slow degradation rate pose significant threats to wildlife, human health, and ecological systems. However, the growing awareness and increased environmental consciousness have led to the development of various green options for substituting plastic. This article delves deep into the sustainable alternatives to plastic, aiming to educate and inspire a shift towards eco-friendly choices.
Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics are emerging as one of the promising substitutes for traditional plastics. Unlike conventional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to break down, biodegradable plastics decompose more quickly when exposed to natural environmental conditions.
Biodegradable plastics are primarily made from natural materials such as corn starch, potato starch, or sugarcane. When disposed of, they break down into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass, causing minimal environmental harm. The transition to biodegradable plastics in various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and medical applications, offers a more sustainable solution compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics.

Plant-Based Plastics
Also known as bioplastics, plant-based plastics are derived from renewable biological sources rather than fossil fuels. Commonly made from polylactic acid (PLA) obtained from fermented plant starch, these plastics offer a greener alternative while maintaining similar properties to conventional plastics.
Comparatively, the production of plant-based plastics results in a lower carbon footprint, as it sequesters carbon dioxide during the growth of the source plants. Furthermore, bioplastics are biodegradable under industrial composting conditions, making them an environmentally friendly option. Their applications are diverse, ranging from disposable cutlery and packaging to automotive components and textiles.
Recycled Materials
Recycling is one of the most effective ways to reduce the demand for new plastic production and minimize waste. Utilizing recycled materials, such as post-consumer plastics, glass, and metals, helps conserve resources and energy, ultimately leading to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Advancements in recycling technology have enabled the production of high-quality recycled plastics that can be used in a myriad of applications. For instance, recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) is commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic bottles, clothing, and packaging materials. By integrating recycled materials into the production process, the environmental footprint of plastic products can be significantly reduced.
Edible Packaging
Edible packaging is a groundbreaking innovation in the quest for sustainable alternatives to plastic. These materials are designed to be consumed along with the product they encase, thereby eliminating waste and packaging disposal concerns.
Edible packaging can be made from various sources, including seaweed, rice, and wheat. A notable example is the use of seaweed-based films to wrap sandwiches and sushi, which are not only biodegradable but also nutritious. Additionally, packaging produced from rice paper or potato starch is gaining popularity for wrapping candies and snacks. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize food packaging and significantly reduce plastic waste.
Natural Fibers and Composites
Natural fibers and composites offer an eco-friendly alternative to plastic in numerous applications. Materials such as bamboo, hemp, jute, and flax are renewable, biodegradable, and have a lower environmental impact compared to synthetic counterparts.
Bamboo, for instance, grows rapidly and requires minimal resources, making it an ideal substitute for plastic in products like cutlery, toothbrushes, and straws. Hemp and flax fibers, on the other hand, can be combined with biodegradable resins to create strong, lightweight composites used in automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries.
Glass and Metal Containers
Glass and metal containers, though not new, are classic and effective alternatives to plastic. These materials are durable, reusable, and infinitely recyclable, making them a sustainable choice for various applications.
Glass is non-toxic and inert, ensuring that it does not leach chemicals into food and beverages. It is particularly effective for packaging liquids and food products. Metal containers, commonly made from aluminum or stainless steel, are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and provide a higher barrier to light and oxygen compared to plastic. Their durability and reusability make them ideal for storing food, beverages, and personal care products.
Paper and Cardboard
Paper and cardboard have been traditional alternatives to plastic packaging, especially in the food and retail industries. These materials are derived from renewable wood pulp and are biodegradable and recyclable, contributing to a closed-loop system.
Innovations in paper and cardboard packaging have led to the development of water-resistant coatings and stronger material properties, expanding their use beyond simple packaging. For example, paper straws, cardboard food containers, and molded pulp packaging for electronics are becoming increasingly popular. The versatility and sustainability of paper and cardboard make them a viable substitute for plastic in numerous applications.

Mushroom Packaging
Mushroom packaging, also known as mycelium packaging, is an innovative and eco-friendly alternative to plastic. This type of packaging is made from the root system of mushrooms and agricultural waste, which are combined and grown into desired shapes.
Mycelium packaging offers several environmental benefits: it is biodegradable, compostable, and requires significantly less energy and resources to produce compared to conventional plastics. It is also effective in absorbing impacts, making it an excellent choice for protective packaging in electronics, furniture, and delicate items. Mushroom packaging exemplifies how nature-inspired solutions can address modern environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The quest for sustainable alternatives to plastic is gaining momentum as awareness of plastic pollution and its impact on the environment increases. A variety of green options, ranging from biodegradable plastics and plant-based materials to natural fibers and innovative packaging solutions, present viable alternatives to conventional plastics. By embracing these eco-friendly substitutes, individuals and industries can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Transitioning to greener options requires a collective effort from consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers. It involves making conscious choices, investing in sustainable technologies, and implementing regulations that promote the use of environmentally friendly materials. As we move towards a more sustainable society, the adoption of green alternatives to plastic will play a crucial role in safeguarding our planet for future generations.
Latest Posts
Essential Tips for Managing Organic Waste